World Top 5 Oil Fields
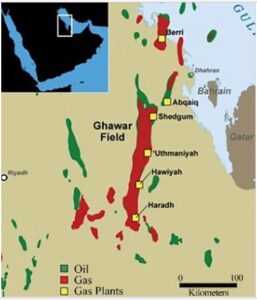
#1 Ghawar Field
The Ghawar Field is the world’s largest oil field, located in Saudi Arabia. It is operated by Saudi Aramco, the state-owned oil company of Saudi Arabia. The field was discovered in 1948 and has been in production since 1951.
Production and Wells
- Daily Production: Approximately 3.8 million barrels of oil per day.
- Wells Drilled: Over 3,000 wells, including oil, gas, and injection wells.
Geological Formations
The Ghawar Field primarily produces oil from carbonate formations, specifically from the Jurassic Arab-D and Hanifa reservoirs.
Arab-D Formation:
- Main producing formation.
- Consists of highly porous and permeable limestone and dolomite.
- Known for its excellent reservoir quality and significant hydrocarbon content.
Hanifa Formation:
- Located below the Arab-D.
- Composed mainly of carbonates, primarily limestone.
- Contributes to the field’s production, though less prolific than the Arab-D.
Processing Plants
Gas-Oil Separation Plants (GOSPs):
- The field is supported by multiple GOSPs that process crude oil and associated gas.
- These plants separate oil, gas, and water, stabilize crude oil, and prepare it for export.
Gas Processing Plants:
- Facilities to process and condition gas for reinjection or export.
- Essential for maintaining reservoir pressure and enhancing oil recovery.
Pipeline Infrastructure
East-West Pipeline:
- Transports crude oil from the Ghawar Field to export terminals on the Red Sea coast.
- Part of Saudi Arabia’s extensive oil export infrastructure.
Crude Oil Specifications
The crude oil from the Ghawar Field is typically classified as light to medium crude oil. Here are the general specifications:
- API Gravity: 32° to 34°, categorized as light to medium crude oil.
- Sulfur Content: Generally low, around 1% to 2%, making it relatively sweet crude.
- Viscosity: Low to moderate, suitable for transportation and processing.
Ownership
The Ghawar Field is owned and operated by Saudi Aramco, which is entirely owned by the Government of Saudi Arabia.
The Ghawar Field is estimated to account for about 6% of the world’s total daily crude oil output.
Summary
The Ghawar Field is a major asset for Saudi Arabia’s oil production, characterized by its vast reserves, light to medium crude oil, and extensive infrastructure. It plays a crucial role in Saudi Arabia’s economy and contributes significantly to the global oil supply.
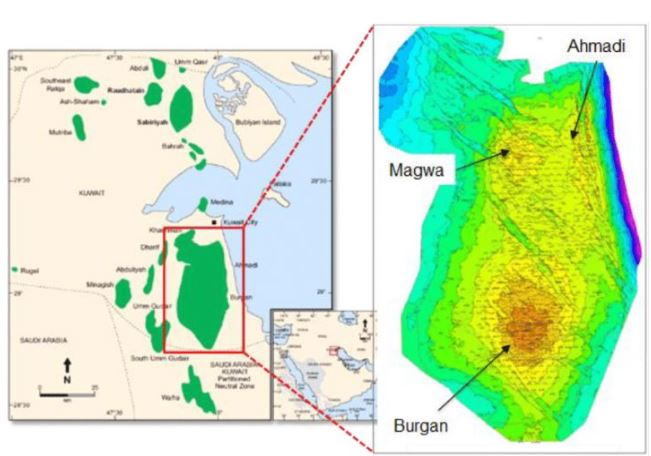
#2 Burgan Field
The Burgan Field is one of the world’s largest oil fields and is located in Kuwait. It is operated by the Kuwait Oil Company (KOC), a subsidiary of the state-owned Kuwait Petroleum Corporation (KPC). The field was discovered in 1938 and has been in production since 1946.
Production and Wells
- Daily Production: Approximately 1.7 million barrels of oil per day.
- Wells Drilled: Over 1,700 wells, including oil, gas, and injection wells.
Geological Formations
The Burgan Field produces oil primarily from Cretaceous formations, with the most significant being the Burgan Formation.
Burgan Formation:
- Main producing formation.
- Consists of sandstone with high porosity and permeability.
- Known for its excellent reservoir properties and significant hydrocarbon content.
Wara Formation:
- Located above the Burgan Formation.
- Also a sandstone reservoir with good reservoir properties.
Mauddud Formation:
- Situated above the Wara Formation.
- Contains limestone and is another important reservoir in the Burgan Field.
Processing Plants
Gathering Centers (GCs):
- The field is supported by multiple gathering centers that process crude oil and associated gas.
- These centers separate oil, gas, and water, stabilize crude oil, and prepare it for export.
Gas Boosting Stations:
- Facilities to boost gas pressure for reinjection or export.
- Essential for maintaining reservoir pressure and enhancing oil recovery.
Pipeline Infrastructure
North and South Pipelines:
- Transport crude oil from the Burgan Field to export terminals and refineries.
- These pipelines are part of Kuwait’s extensive oil export infrastructure.
Crude Oil Specifications
The crude oil from the Burgan Field is typically classified as medium to light crude oil. Here are the general specifications:
- API Gravity: 28° to 35°, categorized as medium to light crude oil.
- Sulfur Content: Generally between 2% and 3%, making it medium-sour crude.
- Viscosity: Moderate, suitable for transportation and processing.
Ownership
The Burgan Field is owned and operated by the Kuwait Oil Company (KOC), which is a subsidiary of the Kuwait Petroleum Corporation (KPC). KPC is entirely owned by the Government of Kuwait.
The Burgan Field is estimated to account for about 6% of the world’s total daily crude oil output.
Summary
The Burgan Field is a major asset for Kuwait’s oil production, characterized by its vast reserves, medium to light crude oil, and extensive infrastructure. It plays a crucial role in Kuwait’s economy and contributes significantly to the global oil supply.
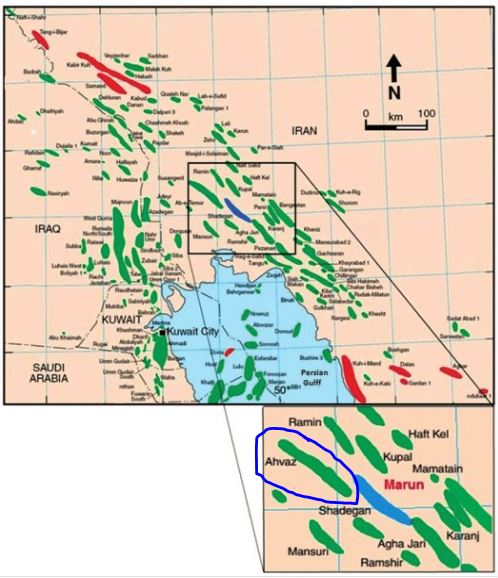
#3 Ahvaz Field
The Ahvaz Field is one of the largest oil fields in Iran and is located in the southwestern part of the country, within the Khuzestan Province. The field is operated by the National Iranian South Oil Company (NISOC), a subsidiary of the National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC). The field was discovered in 1953 and has been a major contributor to Iran’s oil production since then.
Production and Wells
- Daily Production: Approximately 750,000 barrels of oil per day.
- Wells Drilled: Over 500 wells, including oil, gas, and injection wells.
Geological Formations
The Ahvaz Field produces oil from several key formations, predominantly within the Asmari and Bangestan reservoirs.
Asmari Formation:
- The primary producing formation.
- Composed mainly of carbonate rocks, particularly limestone and dolomite.
Known for its excellent porosity and permeability.
Bangestan Formation:
- Located below the Asmari Formation.
- Composed of carbonates, primarily limestone.
- Also significant in terms of hydrocarbon content.
Khami Group:
- Includes several formations, often producing deeper hydrocarbons.
- Contains carbonate reservoirs with significant oil potential.
Processing Plants
Oil Processing Plants:
- Multiple facilities handle the separation of crude oil, natural gas, and water.
- These plants stabilize crude oil and prepare it for transport.
Gas Processing Plants:
- Facilities for processing associated natural gas and recovering valuable natural gas liquids (NGLs).
Pipeline Infrastructure
- Domestic and Export Pipelines:
- The field is connected to a network of pipelines that transport crude oil to domestic refineries and export terminals.
- Major pipelines link the field to the Abadan Refinery and other key facilities.
Crude Oil Specifications
The crude oil produced from the Ahvaz Field is typically characterized as medium to heavy crude oil. Here are the general specifications:
- API Gravity: 22° to 33°, categorized as medium to heavy crude oil.
- Sulfur Content: Typically around 2% to 3%, making it sour crude.
- Viscosity: Moderate to high, affecting transportation and processing requirements.
Ownership
The Ahvaz Field is owned and operated by the National Iranian South Oil Company (NISOC), which is a subsidiary of the National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC). NIOC is fully owned by the Government of Iran.
The Ahvaz Field is estimated to account for approximately 2.5% of the world’s total daily crude oil output.
Summary
The Ahvaz Field is a cornerstone of Iran’s oil production, characterized by its extensive reserves, medium to heavy crude oil, and significant production capacity. It plays a vital role in Iran’s economy and its contributions to the global oil market.
#4 Gachsaran field
 Gachsaran Field Overview
Gachsaran Field Overview
The Gachsaran Field is one of Iran’s largest and most productive oil fields, located in the southwestern part of the country, in the Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad Province. The field is operated by the National Iranian South Oil Company (NISOC), a subsidiary of the National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC). It was discovered in 1928 and has been a significant source of crude oil production since then.
Production and Wells
- Daily Production: Approximately 560,000 barrels of oil per day.
- Wells Drilled: Over 700 wells, including oil, gas, and injection wells.
Geological Formations
The Gachsaran Field primarily produces oil from the Asmari and Bangestan formations, along with contributions from other formations within the Khami Group.
Asmari Formation:
- The main producing formation.
- Composed of carbonate rocks, particularly limestone and dolomite.
- Known for its high porosity and permeability.
Bangestan Formation:
- Located below the Asmari Formation.
- Composed primarily of carbonates, including limestone.
- Contains significant hydrocarbon reserves.
Khami Group:
- Includes several deeper formations with substantial hydrocarbon potential.
- Contains carbonate reservoirs with significant oil and gas reserves.
Processing Plants
Oil Processing Plants:
- Multiple facilities handle the separation of crude oil, natural gas, and water.
- Stabilize crude oil and prepare it for transport and export.
Gas Processing Plants:
- Facilities for processing associated natural gas and recovering valuable natural gas liquids (NGLs).
Pipeline Infrastructure
- Domestic and Export Pipelines:
- The field is connected to a network of pipelines transporting crude oil to domestic refineries and export terminals.
- Major pipelines link the field to the Abadan Refinery and other key facilities.
Crude Oil Specifications
The crude oil produced from the Gachsaran Field is typically characterized as medium to heavy crude oil. Here are the general specifications:
- API Gravity: 20° to 33°, categorized as medium to heavy crude oil.
- Sulfur Content: Typically around 2% to 3%, making it sour crude.
- Viscosity: Moderate to high, influencing transportation and refining processes.
Ownership
The Gachsaran Field is owned and operated by the National Iranian South Oil Company (NISOC), a subsidiary of the National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC). NIOC is entirely owned by the Government of Iran.
The Gachsaran Field is estimated to account for about 1.5% of the world’s total daily crude oil output.
Summary
The Gachsaran Field is a major asset in Iran’s oil production portfolio, known for its extensive reserves, medium to heavy crude oil, and significant production capacity. It plays a crucial role in Iran’s energy sector and its contributions to the global oil market.
#5 Upper Zakum Field
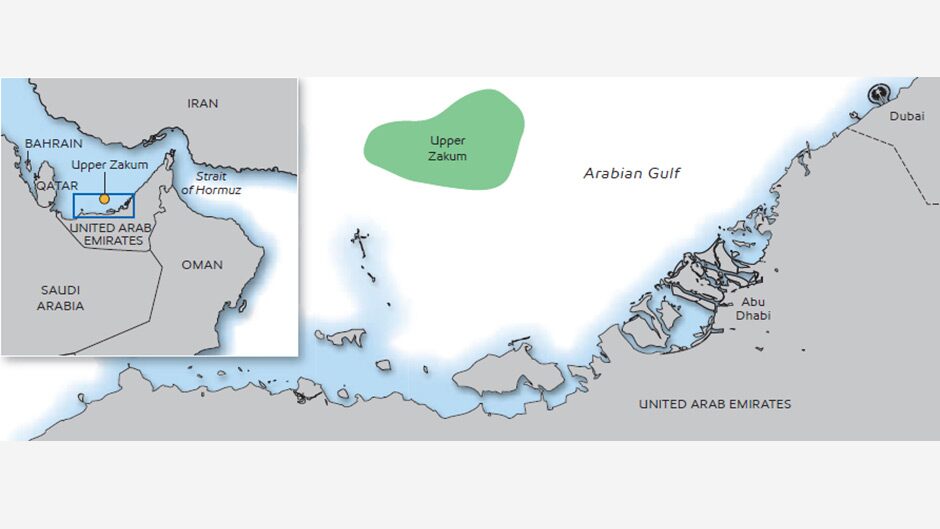
The Upper Zakum Field is one of the largest oil fields in the world and is located offshore in the Persian Gulf, about 84 kilometers northwest of Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. The field is operated by the Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC), and it is a joint venture involving ADNOC, ExxonMobil, and Japan Oil Development Company (JODCO). The field was discovered in 1963 and has been in production since 1982.
Production and Wells
- Daily Production: Approximately 600,000 to 700,000 barrels of oil per day.
- Wells Drilled: Over 350 wells, including production, injection, and observation wells.
Geological Formations
The Upper Zakum Field primarily produces oil from the following key formations:
Upper Zakum Formation:
- The primary producing formation.
- Consists mainly of carbonate rocks, particularly limestone and dolomite.
- Known for its high porosity and permeability.
Lower Zakum Formation:
- Located below the Upper Zakum Formation.
- Also carbonate rock, similar to the Upper Zakum Formation but with different reservoir characteristics.
Bu Hasa Formation:
- Another significant formation in the field.
- Composed of carbonate rocks with considerable oil reserves.
Processing Plants
Offshore Processing Facilities:
- The field is supported by several offshore platforms that handle the initial separation of crude oil, natural gas, and water.
- These platforms prepare crude oil for export and transport.
Onshore Processing Facilities:
- Oil from the Upper Zakum Field is transported to onshore facilities for further processing.
- The onshore facilities handle additional stabilization and treatment of crude oil.
Pipeline Infrastructure
Export Pipelines:
- Crude oil from the Upper Zakum Field is transported via pipelines to the main export terminal.
- The pipelines also link to other facilities for further processing and distribution.
Crude Oil Specifications
The crude oil produced from the Upper Zakum Field is typically classified as light to medium crude oil. Here are the general specifications:
- API Gravity: 32° to 36°, categorized as light to medium crude oil.
- Sulfur Content: Generally low, around 0.5% to 1%, making it a sweet crude.
- Viscosity: Low to moderate, which facilitates transportation and processing.
Ownership
The Upper Zakum Field is operated by ADNOC in partnership with ExxonMobil and Japan Oil Development Company (JODCO). The joint venture structure involves:
- ADNOC: Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (60% ownership).
- ExxonMobil: 28% ownership.
- JODCO: 12% ownership.
The Upper Zakum Field is estimated to account for approximately 2.5% of the world’s total daily crude oil output.
Summary
The Upper Zakum Field is a major asset in the UAE’s oil production portfolio, known for its large reserves, high-quality light to medium crude oil, and significant production capacity. It plays a crucial role in the UAE’s energy sector and its contributions to the global oil market.


Very useful information. Thank you for sharing!
Great Information.
Quite interesting, thanks for laconic information